The measurement methods of self-discharge of lithium-ion batteries are mainly divided into two categories: 1) static measurement method, which obtains the self-discharge rate by standing the battery for a long time; 2) Dynamic measurement method to realize the parameter identification of the battery in the dynamic process.
Static measurement method
At present, the mainstream self-discharge measurement method of lithium-ion batteries is to static the battery for a long time under certain environmental conditions, and measure the change of battery parameters before and after static to characterize the self-discharge degree of lithium-ion batteries. According to the different measurement parameters, static measurement is mainly divided into three categories: capacity measurement, open circuit voltage measurement, and current measurement.
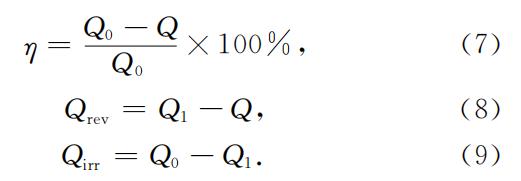
1. Capacity measurement
Before the battery is allowed to stand for a long time, charge and discharge the battery once and record the discharge capacity Q0 before standing. After standing, the battery is discharged in the same way, and the discharge capacity Q after standing is recorded.
According to equation (7), the self-discharge rate η of the battery can be calculated. Then the battery is charged and discharged in the same way, and the battery discharge capacity Q1 after the cycle is recorded. According to equations (8) and (9), the reversible self-discharge Qrev and irreversible self-discharge Qirr of the battery can be calculated respectively. A diagram of the method is shown in Figure 1.
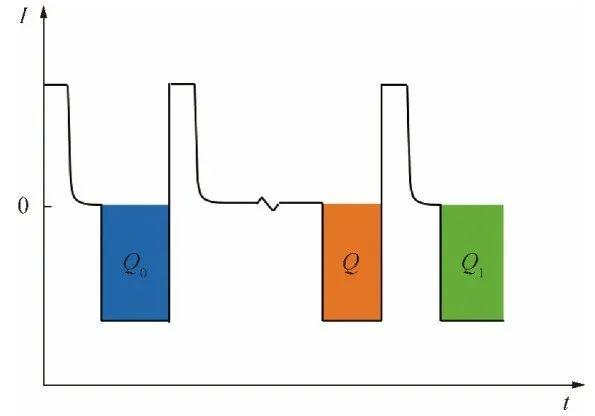
FIG. 1 Schematic diagram of capacity measurement method
In the battery testing manual issued by the international standardization bodies and relevant government departments and industry associations, the relevant provisions are made for the detection of battery self-discharge through capacity measurement: The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) issued "Batteries and battery packs containing alkaline or other non-acidic electrolytes: Portable secondary lithium Batteries and accumulators "(IEC 61960) stipulates that the battery will be in the state of 50%SOC, stored at the ambient temperature of (20±5)℃ for 90 days, and the discharge of the battery after recharging should not be less than 85% of the rated capacity, the specific measurement process is shown in Figure 2a. The battery test manual for electric vehicles issued by the United States Automotive Research Council (USCAR) stipulates that the actual power level corresponding to the operating range of the battery should be measured before measurement. After the battery is discharged at a C/3 ratio of 50% of the available electricity, it is stored at an ambient temperature of 30 ° C for 30 days, and the discharge of the battery is measured after recharging. The "Performance Requirements and Test Methods of power batteries for Electric Vehicles" (GB/T 31486) issued by the Standardization Administration of China is similar to the IEC standard, which stipulates the measurement test process of charge retention and capacity recovery ability. Taking the room temperature test as an example, the battery is stored for 8d at room temperature, the charge retention rate is not less than 85% of the initial capacity, and the capacity recovery is not less than 90% of the initial capacity. The specific measurement process is shown in Figure 2b.
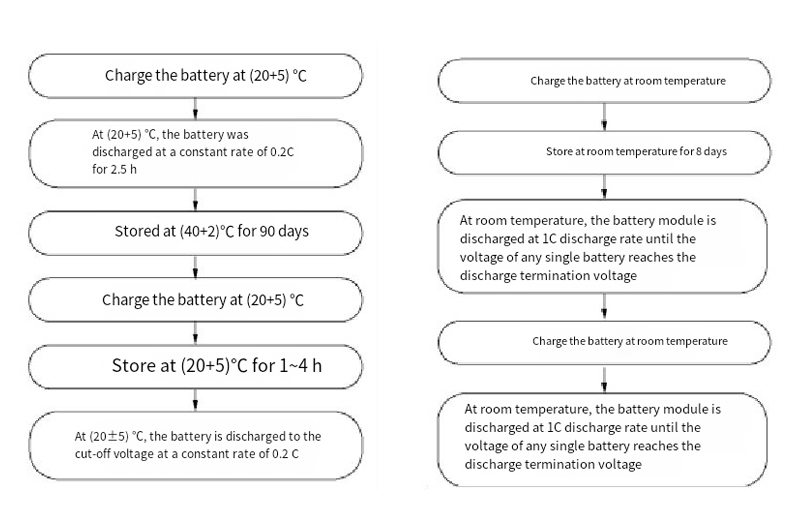
FIG. 2 Measurement procedure (a) specified in IEC 61960 and measurement procedure (b) specified in GB/T 31486
2. Open circuit voltage measurement
The self-discharge degree of lithium-ion battery is characterized by measuring the change of the open-circuit voltage during the battery resting process. The advantage of this method is that it is simpler and less time-consuming than measuring capacity. The disadvantage is that for lithium-ion batteries with a long voltage platform on the open volt-soc curve (such as LFP batteries), the battery voltage changes little in a large SOC range, and it is difficult to characterize the degree of self-discharge by measuring the open voltage, that is, the method has a certain range of application.
3. Current measurement
The lithium-ion battery is charged by micro-current to keep the battery voltage unchanged, and the charging current value when stable is self-discharge current [1-2]. This small current may not be stabilized for several months, and the stability time of different battery designs is different, and the generally recommended measurement time is at least one week [3].
This method has similar problems to the method of measuring open circuit voltage, that is, for lithium-ion batteries with long voltage platforms, the effectiveness of this method is challenged. In addition, because the self-discharge current of lithium-ion batteries is extremely small, generally C/50000 or lower, to apply and measure this tiny order of current, the requirements for experimental instruments are high.
The above conventional static current measurement method is improved to some extent. An electrochemical workstation is used to apply a constant voltage lower than the open current to the battery, and the current flowing through the circuit is measured at the same time. The current-time curve of the battery without self-discharge and the battery with self-discharge is shown in Figure 3a.
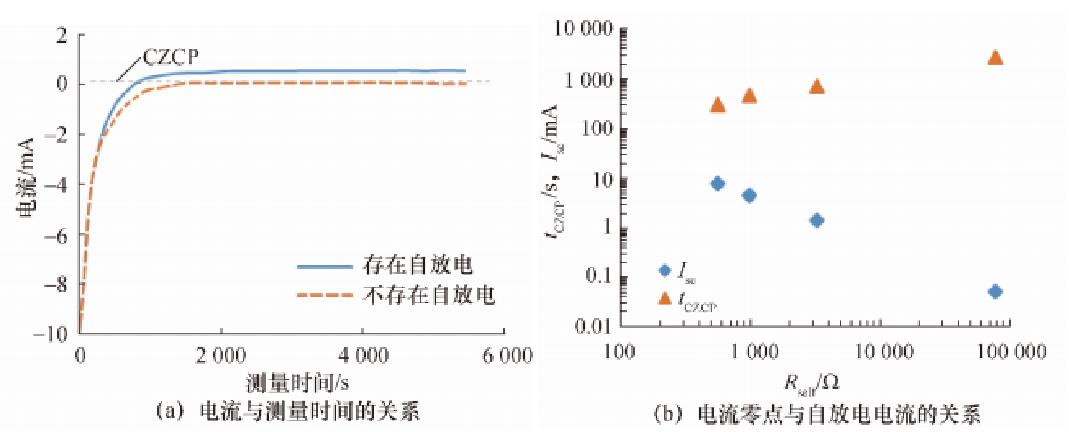
FIG. 3 Partial experimental results of Sazhin current measurement method
By actively applying a constant voltage, controlling the battery to reach the equilibrium state, and, measuring the current flowing through the circuit during this process, the measurement time can be shortened. In addition, the crossing point (CZCP) where the current is zero can also be used as a parameter to characterize the self-discharge rate. As shown in Figure 3b, the logarithm of tCZCP when the current Isc reaches zero is positively correlated with the logarithm of the self-discharge resistance Rself.
However, this method also has a serious disadvantage, that is, the accuracy of the experimental equipment is high. The electrochemical workstation used in the experiment has a voltage resolution of 100uV(14.5V range) and a current resolution of 1pA(200nA range).
Taken together, the above three methods are very time-consuming, with the experimental period ranging from one day to tens of days, and the reduction of the measurement time in the current measurement scenario requires high equipment costs.
Dynamic measurement method
Dynamic measurement method, that is, to realize the parameter identification of the battery in the dynamic process. To shorten the measurement time, save space resources and human resources. One method is to speed up the self-discharge rate by changing conditions such as the ambient temperature and SOC of the battery, so that the measurement parameters can change relatively large in a short period. Although this method saves the experiment time, it also speeds up the aging of the battery and increases the damage to the battery, which is only suitable for laboratory research and is not suitable for large-scale applications in actual production. Another method is to introduce self-discharge resistance based on the existing mature lithium-ion battery equivalent circuit model, and measure the self-discharge rate of lithium-ion batteries in the dynamic process through different parameter identification means.
Based on the automatic system identification theory, the lithium-ion battery is simplified into a first-order resistance-capacitance (R-C) equivalent circuit, and the same charge and discharge current is applied to the lithium-ion battery and the equivalent circuit, and the parameters of the equivalent circuit are adjusted according to the difference in output voltage until the difference between the two approaches zero, and the self-discharge resistance value of the lithium-ion battery is obtained. The total measurement time required for this method is about 12h. However, this method equates the battery to a passive circuit and does not consider the influence of the change of the battery's state of charge on the output voltage during the experiment.
Reduce the battery to an equivalent circuit as shown in Figure 4. Where: Rp, i is the electrochemical reaction resistance, Cp, i is the double electric layer capacitor, Rself is the self-discharge resistance, and C is the battery equivalent capacitance. Applying a short-time current pulse to the lithium-ion battery measures the voltage change during the subsequent resting process, and the self-discharge resistance value is further analyzed. This method only considers the reaction that plays a leading role in each stage of the static process and decouples the complex reactants, reducing the calculation and shortening the measurement time.
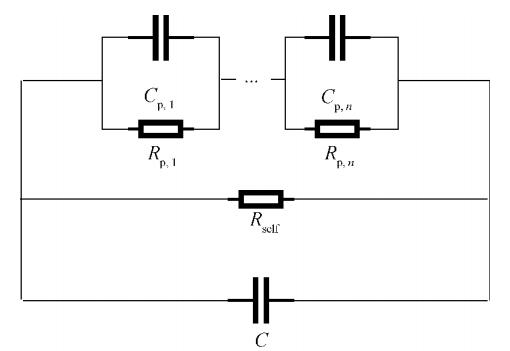
Figure 4 Lithium-ion battery equivalent circuit
Plus précisément, la récupération de la surtension joue un rôle prépondérant dans la phase initiale de statique, et l'autodécharge de la batterie en fin de statique joue un rôle prépondérant. La constante de temps de l'autodécharge peut être analysée par les données à la fin de la période statique, puis la chute de tension causée par l'autodécharge pendant la période de récupération de la surtension peut être compensée, et la capacité équivalente de la batterie peut être résolu, et la valeur de résistance à l'auto-décharge peut être obtenue. Cette méthode peut obtenir la résistance à l'autodécharge des batteries lithium-ion en 10 ~ 48h, ce qui permet de gagner beaucoup de temps par rapport à la méthode traditionnelle, mais elle doit encore consommer beaucoup de temps statique pour observer l'étape où l'autodécharge joue. un rôle dominant.
L'effet d'un court-circuit dans la batterie est divisé en deux catégories : effet paramètre et effet consommation. Parmi eux : l'effet de paramètre signifie qu'en raison de l'existence d'une résistance de court-circuit, la tension de circuit ouvert mesurée et la résistance interne présentent un certain écart par rapport à la valeur réelle ; L'effet de consommation signifie qu'en raison de l'existence d'une résistance aux courts-circuits, l'énergie stockée à l'intérieur de la batterie est consommée en continu et que le SOC de la batterie continue de diminuer, ce qui entraînera un certain écart de la valeur réelle de la tension de circuit ouvert de la batterie et résistance interne de la valeur normale.
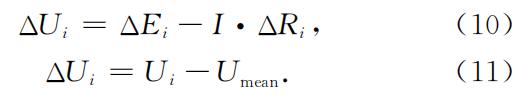
Dans le modèle de différence de batterie illustré dans les formules (10) et (11), Ei est la tension en circuit ouvert de la batterie, Ri est la résistance interne de la batterie et Ui et I sont respectivement la tension et le courant mesurés de la batterie. Les valeurs de ΔEi et ΔRi sont obtenues par la méthode des moindres carrés récursifs, et les paramètres anormaux dépassant le seuil sont identifiés par une méthode statistique pour déterminer si la batterie présente un court-circuit interne. Lorsque la résistance de court-circuit est de 100Ω, la méthode peut réaliser l'identification du court-circuit interne en 4h43min au plus tôt.
Les trois méthodes de mesure dynamique ci-dessus simplifient la batterie lithium-ion en introduisant des circuits équivalents et d'autres moyens et adoptent des méthodes expérimentales innovantes pour analyser la valeur de résistance à l'autodécharge, qui a fait de grands progrès en raccourcissant le temps de mesure.
Résumer
Les méthodes de mesure du taux d'autodécharge des batteries lithium-ion par mesure statique et mesure dynamique sont passées en revue. Les principales conclusions sont les suivantes:
1, la réaction secondaire se produisant à l'interface électrode négative/électrolyte et électrode positive/électrolyte est la principale source d'autodécharge de la batterie lithium-ion, peut être modifiée par la surface de l'électrode positive, l'ajout d'additifs dans l'électrode négative , électrolyte et autres moyens pour inhiber l'apparition de l'autodécharge.
2, dans le processus de stockage de la batterie, devrait essayer d'éviter d'être dans un état SOC trop élevé ou trop bas, et la température et l'humidité ambiantes doivent être maintenues dans une plage relativement basse.
3. La méthode actuelle de mesure de l'autodécharge est une mesure statique basée sur une expérience statique à long terme. Le plus gros problème avec cette méthode est que le temps de mesure est trop long, ce qui entraîne un énorme gaspillage d'espace et de ressources humaines. Certaines méthodes de mesure dynamique pour l'identification des paramètres combinées à des modèles de circuits équivalents ont été proposées, et certains progrès ont été réalisés dans le raccourcissement du temps de mesure. Grâce à une conception expérimentale innovante, l'identification du découplage de l'autodécharge dans le processus dynamique est la voie clé et la direction de développement pour réaliser une mesure rapide de l'autodécharge à l'avenir.
Catégories
récent messages
Scannez vers WeChat:everexceed
